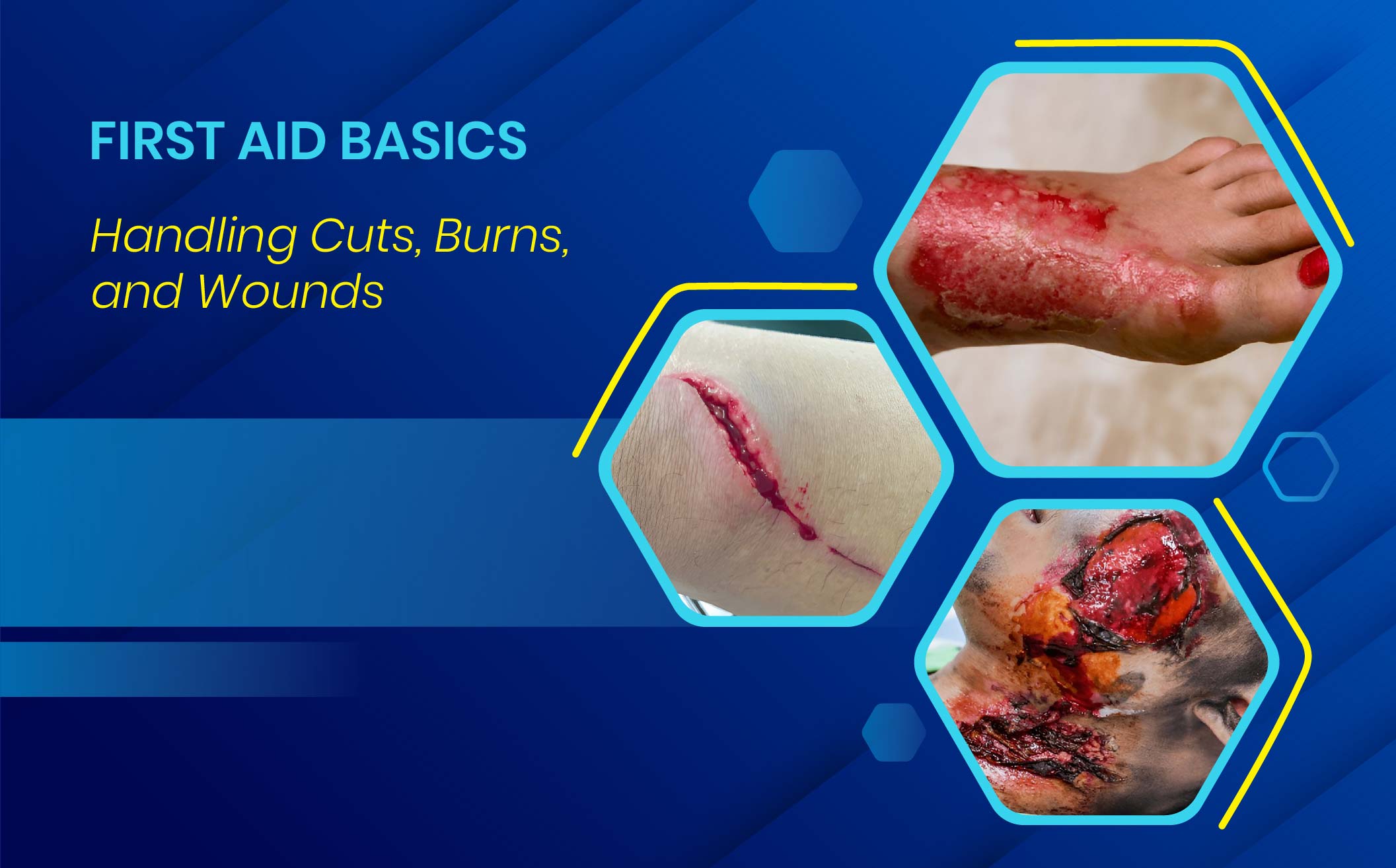
Basic knowledge of first aid can help treat cuts, burns, and wounds with a golden minute count. Whether you are dealing with a small scrape or a deep laceration, knowing the correct first aid will provide quick action to prevent infections and promote healing. Whether you need to stop bleeding or take care of a wound, this guide discusses critical first-aid techniques to help you manage injuries effectively and safely. Continue reading on how to treat it best and what supplies need to be stocked in your first aid kit.
First Aid Essentials: Treating Cuts, Burns, and Wounds
I. Cuts and Wounds
A. What Are Cuts and Wounds?
What exactly is a cut? Fundamentally, a cut is a break in the skin that can happen for a whole variety of reasons, including, but not limited to, sharp objects like knives or glass. A scrape and a laceration, on the other hand, are distinct from a cut, which typically has a straight edge. Scrapes are surface injuries, most often caused by friction with rough surfaces; lacerations are deeper tears in the skin that may penetrate into muscle or fat. Knowing these contrasts is crucial for identifying the appropriate treatment.
There were 2 types of common wounds: Open and closed. Open wounds break the skin and underlying tissue, whereas closed wounds do not break the skin (contusions or bruises), but can cause considerable damage beneath the surface.
B. Typical Causes of Cuts and Wounds
Anyone, anywhere, can get cuts and wounds. Common mishaps — cutting yourself while chopping vegetables, falling while walking, or accidentally knocking something over — alsocause injury.
Occupational hazards are another common source, particularly for those in jobs that require sharp instruments or heavy machinery. Not to mention recreational pursuits! Whether on a weekend hike, playing sports — or even just horsing around with friends — the risk of injury is never too far away.
C. Recognizing Severity
It is also important to know how to assess the seriousness of a cut or wound. A minor cut typically bleeds lightly and only needs basic first aid. But it’s important to evaluate the depth and place of the wound. A deep cut, especially one that bleeds heavily, or seeing muscle or fat may be crystal clear clues that medical care is needed. If you are unsure, it is best to be cautious and talk to a doctor.
Why risk infection for minor cuts? Act fast, prevent complications, clean, disinfect, and protect with Cimidaxil FirstAid. Always have it in your first-aid kit! Whether at home, work, or outdoors, it all begins with preparation. Keep ahead of infections and slow healing with Cimidaxil FirstAid!

II. First Aid for Cuts: The Basics
A. Initial Assessment
Assess the affected area When you have a cut, the first step is to assess the area that was affected. Check for bleeding what kind of wound it is and if you see any sign of complications. like abnormal pain or swelling. To properly provide first aid for cuts, the first step is to identify if the cut is minor or if medical attention is needed. If you suspect there may be an underlying tissue injury (like a cut to a nerve or tendon) or if it is bleeding profusely, don’t hesitate to get seen.
B. Controlling Bleeding
Applying direct pressure over the wound with a clean cloth or bandage helps to control bleeding. If you don’t have a bandage at hand, a clean piece of clothing can also do the trick. Raising an injured area of the body may also slow bleeding by minimizing blood flow in that area. Just make sure you apply that pressure consistently!
C. Cleaning the Wound
It is important to clean the wound so that it does not get infected. Rinse out dirt and debris using clean, running water. Soap and water—mild soap, please — can be helpful, but don’t scrub too hard. Here’s a trick if you have antiseptic wipes: Wipe the area gently (to further reduce risk), and pat it dry with a clean cloth.
Protect, heal, and recover faster with Cimidaxil FirstAid! Be ready for any cut or wound with instant protection and infection control. Get Cimidaxil FirstAid today and stay safe, wherever you go!

First Aid for Wounds: Essential Steps
When used for first aid for wounds, the first step is to rinse the wound with clean water or saline. Use direct pressure to help stop any bleeding, then cover the wound with a clean bandage or dressing. Watch for early signs of infection, like redness or swelling, and go to a doctor when needed.
Why First Aid for Wounds Matters
Have Severe Wounds Proper First Aid Proper first aid for wounds can go a long way in not only preventing complications but also promoting faster healing. Make sure you have a first aid kit and know the principles of wound care, so you can respond in case of an accident.
III. First Aid Treatment for Various Wound Types
A. Abrasions and Scrapes
For smaller abrasions, your initial step is cleaning, as discussed above. After cleaning, a mild ointment can help relax the area. Monitor for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling or pus, and seek help if they occur.
B. Lacerations
It is important to know if a laceration requires stitches. If the cut is deep, gaping wider than half an inch or won’t stop bleeding, it’s probably time to get professional help. “We can manage them at home for shallower cuts using butterfly bandages or adhesive strips.” Over-the-counter pain relievers, for example, may help with pain management.
C. Puncture Wounds
Puncture wounds, caused by something like a nail or a bite, can be tricky. They usually don’t bleed a lot but can deliver bacteria deep into the skin. Also watch for symptoms of infection or signs of tetanus, especially if the object was dirty. In addition to cleaning and monitoring for infection, a healthcare provider may need to assess these wounds.
No matter the wound—abrasion, laceration, or puncture—Cimidaxil FirstAid has you covered! Ensure fast healing and infection protection with our trusted first-aid solution. Stay prepared—get Cimidaxil FirstAid today!

IV. First Aid for Bleeding Wounds: Techniques
A. First Aid for Bleeding
If you are bleeding, apply direct pressure with a clean cloth or bandage to keep the blood from flowing. If you can, elevate the injured area and apply pressure until the bleeding stops. For heavy bleeding, call for immediate medical attention. Proper first-aid treatment for bleeding can prevent complications and promote faster healing. Always prioritize safety and cleanliness.
B. Applying Direct Pressure
Direct pressure is the best way to start controlling bleeding. What you want to do is apply firm, continuous pressure with a clean dressing or gauze. If the dressing gets soaked through, don’t take it off; put another one on top of that to keep pressure and absorb more blood.
C. Using Pressure Points
Knowing pressure points also is useful in more extreme situations. Larger arteries bring blood relatively close to the skin’s surface, so applying pressure in the right spots can slow bleeding significantly. For instance, pressing on the second fold of the inner elbow, approximately where a blood draw would take place, can alleviate bleeding from an arm injury.
D. Tourniquet Application
A tourniquet may be needed in severe cases. Only use this as a last resort. It’s important to show how to use it properly: above the wound, not on it, and tighten until the bleeding stops. But keep in mind that the longer you use it, the more they can damage the tissue, so it’s paramount to seek help ASAP after the application.
Cimidaxil FirstAid — Ensure An Effective Control Of Bleeding Whether applying direct pressure or providing emergency care, our first-aid solution makes you act quickly. Extra — prepare yourself — grab Cimidaxil FirstAid now!

V. Post-Treatment Care and Wound Prevention
A. How You Monitor the Healing Process
Flairs can be activated when a wound is treated, so watch the wound! Normal healing should be getting better slowly, with little or no discomfort. Be sure to change the bandages often, preferably once every day or when they become wet or dirty, while keeping the area clean and under dry conditions to promote healing.
B. Preventing Future Injuries
It’s never too late to understand how future incidents can be avoided. Follow safety precautions at home, wear protective equipment at work or during sports or hobbies, and urge family members to take first-aid classes. Information is power, especially in an emergency!
C. First Aid Supplies for Cuts and Scrapes
A well-stocked first-aid kit can make all the difference. Basic items include bandages, antiseptic wipes, gauze, adhesive tape and gloves. Regularly check your kit to replace items that are out of date or expired.
Heal faster and stay prepared with Cimidaxil FirstAid! Keep wounds clean, change bandages regularly, and prevent infections with our trusted first-aid solution. Stock up on Cimidaxil FirstAid for complete wound care!

VI. First Aid for Burns
For small burns/boils, rinse under running water for 10-15 minutes. Do not use ice or oily substances. Cover with a sterile, non-stick bandage. For serious burns, call emergency medical services immediately, and do not try to pull off any stuck clothing. Proper first aid for burns can reduce pain and prevent further damage. Always prioritize safety and seek medical attention if needed.
A. First Aid for Burns
For chemical burns, rinse the area with water for at least 20 minutes and remove contaminated clothing. Electrical burns: If safe to do so, turn off the power before aiding the victim. Don’t pop blisters or use creams. Having quick and correct first aid for burns is important, to reduce the injury and facilitate recovery. Stay calm and act promptly.
Conclusion
Proper first aid for cuts, wounds, burns, and bleeding can prevent infections and promote faster healing. Clean the wound, apply pressure to stop bleeding, and use antiseptic to reduce infection risk. For severe injuries, seek medical help immediately. Keeping a first aid kit for cuts and wounds handy ensures quick response to emergencies. Prioritizing wound care minimizes complications and aids recovery. Always follow proper first aid procedures for burns and bleeding for safety.